1. Exploring Life and Science
• The Characteristics of Life- All living things are called organisms because each shares common characteristics. Each has the same level of organizations such as atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ system, organism, populations, community, ecosystems, biosphere and all grow and develop. Life has an evolutionary history meaning that all organism share the same characteristic of life because their ancestry can be traced to cells but each organism are diverse from each other because they each adapt to life in a different ways.
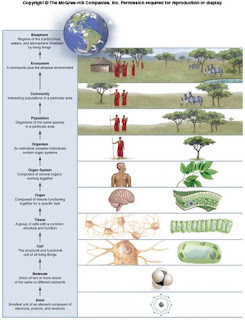 • Human Related to Other Animals- All living things are categorize in kingdoms. Human are vertebrates in the kingdom of animalia. Humans are closed related to apes but did not evolve from apes. Since all living things are included in the biosphere human are probably the biggest threats to the biosphere.
• Human Related to Other Animals- All living things are categorize in kingdoms. Human are vertebrates in the kingdom of animalia. Humans are closed related to apes but did not evolve from apes. Since all living things are included in the biosphere human are probably the biggest threats to the biosphere.• Science as a Process- To understand science it takes time and research. A scientific method is making an observation, making a hypothesis, experiments, conclusion and the developing a theory with the findings.
• Making Sense of a Scientific Study-making a scientific study can take months or years and can change with new findings and other studies. Graphs are usually included with studies. The data is part of the experiment usual a bar or line graph are used to determine the outcome of the experiment. The hypothesis has a chance of having a different outcome at the end and can alter.
• Science and Social Responsibility-Being part of the biosphere, being part of life, everyone is responsible for life and out earth. Today there are many technology and scientists are gaining a better understand about environment, animals, plants and how we can better our future for living.
2. Chemistry of Life
• From Atom to Molecules- Elements is one of the basic building blocks of matter, the human body is composed with four elements: carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen. An atom is the smallest unit of an element. Even though an atom is very small to the human eye it contains even smaller subatomic particles-protons (+charge), neutrons and electrons (-charge). Atoms bond with another form of chemical unit called the molecules. There are two types of bonds, a Ionic bond (ions-+and-charges) and a covalent bonding.
• Water and Living things- Water is the most abundant molecules in living organisms and water is a polar molecule. The human body (blood fills our arteries and veins) is 92% water. Water has different properties such as; water is liquid, water heats and freezes slowly, frozen water is less dense that liquid water, so ice floats on water, water is cohesive and fills tubular vessels, water is also universal solvent, and has a neutral pH. The interesting part about this section was the topic acid and it’s effect. Acid can effect out environment such as rain. Because of burning gasoline (cars) acid is in the air that rises and comes back down with the rain, leaving it hard for crops to grow to their full growth and casing damages to historical statues.
• Molecules of Life- There are four categories of organic molecules, which are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid and are all macromolecules that each contains subunits.
• Carbohydrates-Carbohydrates are quick and short-term energy storage in all livings things.
• Lipids- Lipids are fat and oils, which function in long-term energy storage. The Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated.
• Proteins- Proteins are important in the structure and functions of cells. Their functions are: support, enzymes, transport, defense, hormones and motion. Proteins are macromolecules with amino acid subunit.
• Nucleic Acids- There are two type of nucleic acid, DNA and RNA. Each DNA has different genes.
3. Cell Structure and Function
• What is a Cell? Everything with life is composed with cells and is very small. Most cells can be seen through a microscope
 . The reason why cells are so very tiny is that the surface-area-to-volume radio of a cell.
. The reason why cells are so very tiny is that the surface-area-to-volume radio of a cell.• How cells are organized- A cell is surround by a plasma membrane and has a central nucleus. Between the plasma membrane and central nucleus is a cytoplasm that contains various organelle and each have a specific function.
• The Plasma membrane and how Substance Cross it- All cells are surrounded by an outer plasma membrane and are the boundaries between the outside and inside of a cell.

• The Nucleus and the Production of Protein- the nucleus stores genetic information. Each person has different type of genes theses genes are DNA.
• The Cytoskeleton and Cell Movement- The cytoskeleton contains three types of fiber: microtubules, actins filaments and intermediate filaments. All each help maintain the cell’s shape and allows organelles to move about the cell.
-Cilia and flagella are both part of movement and contain microtubules.
• Mitochondria and Cellular Metabolism-

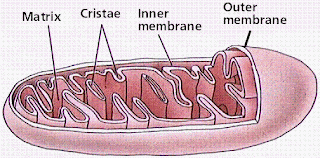
Mitochondria and cellular metabolism are often called the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that forms cristae, which project into the matrix.
4. Organizations and Regulation of Body and Systems-
Types of Tissues- A tissue is composed of specialized cells of the same type that perform a common function in the body. There are four major types that are: connective tissue, muscular tissue, nervous tissue and epithdial tissue.
-Cancer is classified to the type of tissue from which they arise.
Connective tissue Connects and Supports- There are three type of connective tissue: fibrous, supportive tissue and fluid connective tissue.
-The fibrous connective tissue has two tissues and they are loose fibrous and dense fibrous connective tissues.
-The loose fibrous create loose and opens framework. It supports main internal organs like the lungs, arteries and the urinary bladder. It forms a protective covering the organs like the muscles, blood vessels and nerves.
-The dense fibrous connective tissue contains many collagen fibers that are packed together. It has more specific functions and is located in the tendons that connect muscle to bone. Ligaments connect bones to other bones to joints.
Supportive connective tissue-There is three types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, which is the most common and contains fine collagen fibers. It is found in the nose and the end of the ribs. The fetal skeleton contains this hyaline cartilage but later it is replaced with bones. The elastic cartilage is an elastic fibers and is found in the outer ear also is more flexible. Fibro cartilage has a matrix (ground substance and fibers) containing collagen fibers. It is found in structures that withstand tension and pressure, like in the wedges in the knee joint.
-Bone- is the most rigid connective tissue. The compact bone makes up the shaft of the long bone. The end of the long bone contains spongy bone. The spongy bone is designed for strength but is lighter than the compact bone.
Fluid connective tissue- The body has two types of fluid, blood and lymph. Blood is located in the blood vessels and consisted of formed elements and plasma. The lymph contains white blood cells and carried by lymphatic vessels and is derived from tissue fluid.
Muscular Tissue Moves the Body- the muscular tissue is composed by cells called muscle fibers. There is three type of vertebrate muscles tissue: the skeletal, smooth and cardiac.
Skeletal muscle Its function is the movement of the body, is voluntary and has striated (or striped appearance) cells. It has multiple nuclei and is attached to the skeleton.
Smooth muscle its function is in movement of substance in lumen of the body (intestine, bladder and other internal organ), it is involuntary and has spindle-shaped cells each with single nucleus. It is found in blood vessel walls and walls of the digestive tract.
Cardiac muscle its function is pumping blood and is located in the walls of the heart. It has branching striated cells each with a single nucleus and it is involuntary. It has combine features of smooth and skeletal muscles.
Nervous Tissue Communicates- Nervous tissue consists of nerve cells called neurons and neuroglia, the cells that support and nourish the neurons.
Neurons is a cell that has three parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon.
-Dendrates is an extension that receives signal from sensory receptors or other neurons.
-The cell body contains most of the cell’s cytoplasm and the nucleus.
-An axon is an extension that conducts nerve impulses.
Neuroglia are cells that outnumber neurons nine to one and take p more than half the volume of the brain. It support and nourish neurons and form myelin sheaths. They are found in the brain.
Epithelial Tissue Projects- consists of tightly packed cells that form a continuous layer and it covers surfaces and lines body cavities.
Types of epithelia-
Simple epithelia- There is three type of simple epithelium: squamous (located lining in the air sacs of lungs and walls of blood vessels and composed of flattened cells), cuboidal (located in the glands, lining of kidney tubules and composed of cube-shaped cells) and the columnar (located in the lining of small intestine and near the bottom of each cell and composed of rectangular cells) epithelium.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium- It appears to be layered and has irregularly placed nuclei.
Transitional Epithelium- changes in response to tension.
Stratified Epithelia- have many layers of cells, with only the bottom layer touching the basement membrane.
Glandular Epithelia-secretes a product either into ducts or into the blood.
Cell Junctions- There is three ty
 pe of junctions: the tight junctions (are like zipperlike fastenings between cells and prevent leaks) adhesion junction (permit cells to stretch and bend) gap junctions (allows small molecules and signal to pass between cells).
pe of junctions: the tight junctions (are like zipperlike fastenings between cells and prevent leaks) adhesion junction (permit cells to stretch and bend) gap junctions (allows small molecules and signal to pass between cells).Integumentary System-
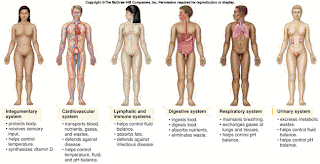
Skin is the most conspicuous system in the body because it covers the body. The skin has two major regions the epidermis and the dermis. Under the skin is the subcutaneous layer. The functions of the integumentary system is to project the body and help regulate body temperature.

Organ Systems-
-Body cavities- The two major body cavities: the ventral and the dorsal cavity.
-dorsal cavity- cranial cavity
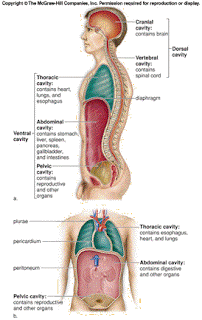 (contains brain) and vertebral canal (contains spinal cord).
(contains brain) and vertebral canal (contains spinal cord).-ventral cavity- thoracic (contains esophagus, heart, and lungs) and abdominal cavity (contains digestive and other organs).
-Body membranes- lines cavities and the internal spaces of organs and tubes
That open to the outside. It has four types:
-Mucous membranes-
-Serous membranes-
-Synovial membranes-
-Meninges-
Homeostasis-
Homeostasis is the body’s ability to maintain a relative constancy of its internal environment by adjusting its physiological processes. All organ systems supply

No comments:
Post a Comment